Research Topics
The Risselada group employs molecular simulation techniques to tackle relevant problems in the field of biophysics and related molecular fields within a multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary research environment (e.g., the Resolv excellence cluster).

Particularly, we focus on the development of enhanced sampling and multiscale methods to study phenomena occurring at fluid (e.g., biological lipid membranes) and solid interfaces (e.g., metal interfaces and graphene). An important current focuses is on a subject coined "facial recognition of fluid interfaces", i.e., how can (bio)molecules optimally recognize and bind fluid interfaces despite their highly disordered and dynamic nature. To this aim, we develop evolutionary molecular dynamics simulations (evo-MD) methods which couple evolutionary algorithms (sampling of chemical space) to coarse-grained molecular dynamic simulations (sampling of phase-space) to resolve the global optima in chemical space. In essence, evo-MD enables molecules to adapt themselves to optimally recognize fluid interfaces in the course of a simulated evolution. Our research may yield unique insights on how biomolecules such as peptides and proteins recognize distinct fluid features in biological lipid membranes with interesting applications for the fields of drug design, surfactant design, and the design of (bio)sensors.
Protein-mediated membrane fusion
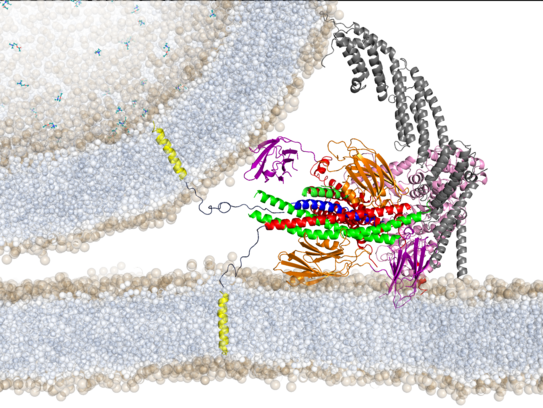
Selected publications
- E.M. Blokhuis, M. D'Agostino, A. Mayer, H.J. Risselada
Fusion pores live on the edge
J. Chem. Phys. Lett., 11(4):1204–1208, 2020 - Y.G. Smirnova, H.J. Risselada, M. Müller
Thermodynamically reversible paths of the first fusion intermediate reveal an important role for membrane anchors of fusion proteins
PNAS 116(7): 2571-2576, 2019 - M. D'Agostino, H. J. Risselada, A. Lürick, C. Ungermann, and A. Mayer
A tethering complex drives the terminal stage of SNARE-dependent membrane fusion
Nature, 551: 634-638, 2017 - M. D'Agostino, H.J. Risselada, A. Mayer
Steric hindrance of SNARE transmembrane domain organization impairs the hemifusion-to-fusion transition
EMBO reports, 17(11):1590-1608, 2016 - H.J. Risselada
Simulations Move Toward a Cure for Viral Diseases
Structure, 23(3):439-440, 2015 - H.J. Risselada, Y. Smirnova, H. Grubmüller
Free energy landscape of rim-pore expansion in membrane fusion
Biophys. J., 107: 2287-2295, 2014 - H.J. Risselada, G. Bubnis, H. Grubmüller
Expansion of the fusion stalk and its implication for biological membrane fusion
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 111:11043-110487, 2014
Latteral organisation of membranes
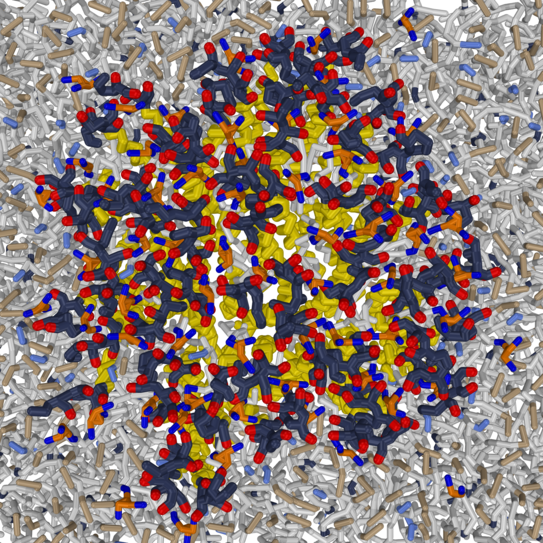
Selected publications
- H.J. Risselada
Membrane fusion stalks and 'lipid rafts': A love-hate Relationship
Biophysical J. (Letter), 112(12): 2475-2478, 2017 - D. Milovanovic, A. Honigmann,..., H.J. Risselada, ..., S.W. Hell, G. Van den Bogaart, R. Jahn
Hydrophobic mismatch sorts SNARE proteins into distinct membrane domains
Nature communications, 6:5984, 2015 - T. Fischer, H.J. Risselada, R.L.C Vink
Membrane lateral structure: The influence of immobilized particles on domain size
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 14:14500-14508, 2012 - G. Van den Bogaart, K. Meyenberg K, H.J. Risselada, H. Amin, K.I. Willig, B.E. Hubrich, M. Dier, S.W. Hell, H. Grubmüller, U. Diederichsen, R. Jahn
Membrane protein sequestering by ionic protein-lipid Interactions
Nature, 479:552-55, 2011 - H.J. Risselada, S.J. Marrink, M. Müller
Curvature-dependent elastic properties of liquid-ordered domains result in inverted domain sorting on uni-axially compressed vesicles
Phys. Rev. Lett., 106: 148102, 2011
Soft (bio)materials @ solid surfaces
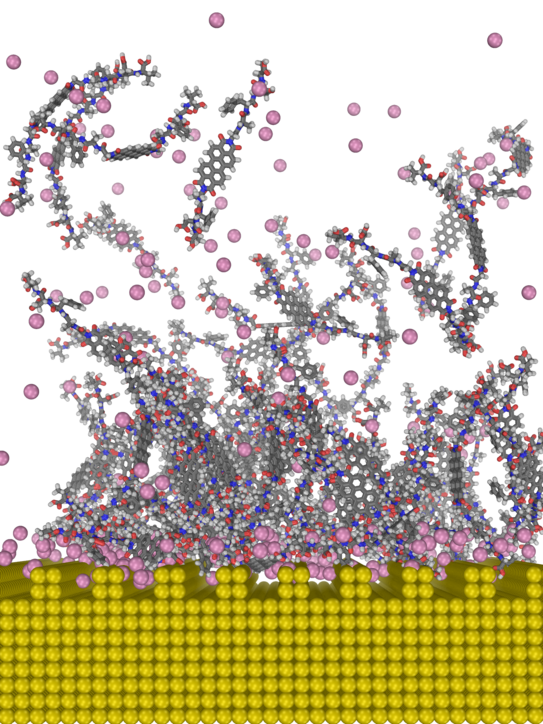
Selected publications
- L.A. Belyaeva, L. Jiang, A. Soleimani, J. Methorst, H.J. Risselada, G.F. Schneider
Liquids relax and unify strain in graphene
Nat. Comm. 11(898), 2020 - A. Gladytz, B. Abel, H.J. Risselada
Gold-Induced Fibril Growth:The Mechanism of Surface-Facilitated Amyloid Aggregation
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55:12242-46, 2016
Morphologies of (bioinspired) surfactant assemblies

Selected publications
- Laura J. Endter, H.J. Risselada
Where are those lipidic nano rings?
J. Colloid Interface Sci., 587:789-796, 2020
- Laura J. Endter, Y.G.Smirnova, H.J. Risselada
Density Field Thermodynamic Integration (DFTI): A ’soft’ approach to calculate the free energy of surfactant self-assemblies
J. Phys. Chem. B, 124(31):6775–6785, 2020